Solved Exercise 6.10 (Poisson approximation of Binomial RV).
PPT Lecture Slides PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6600397
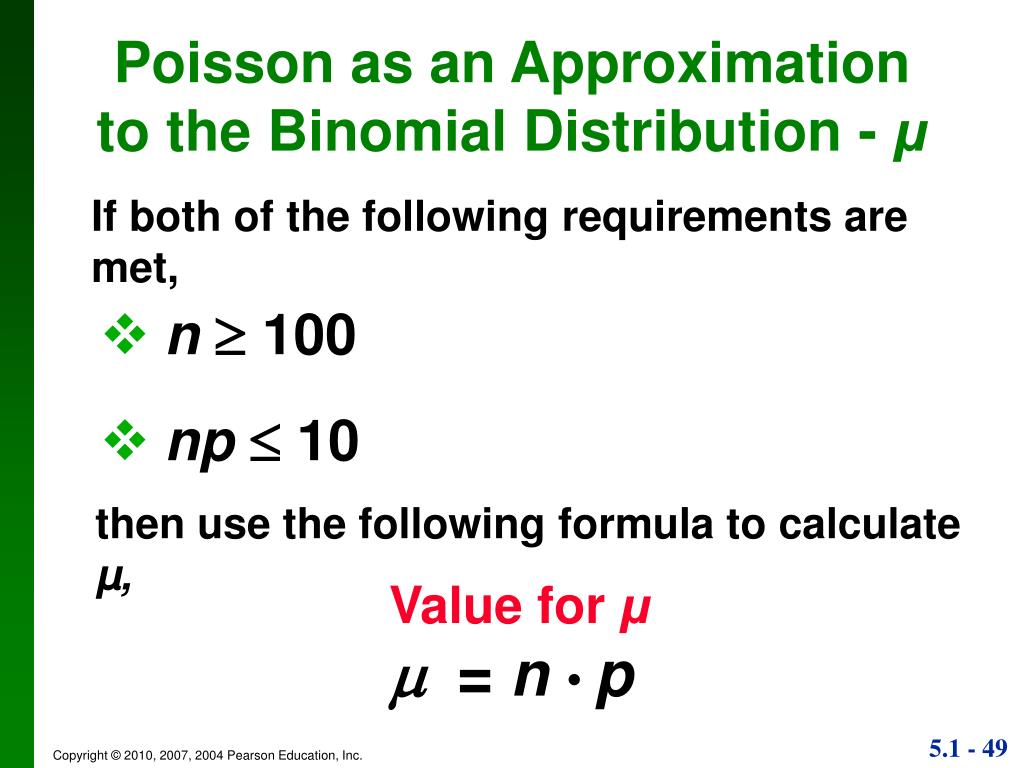
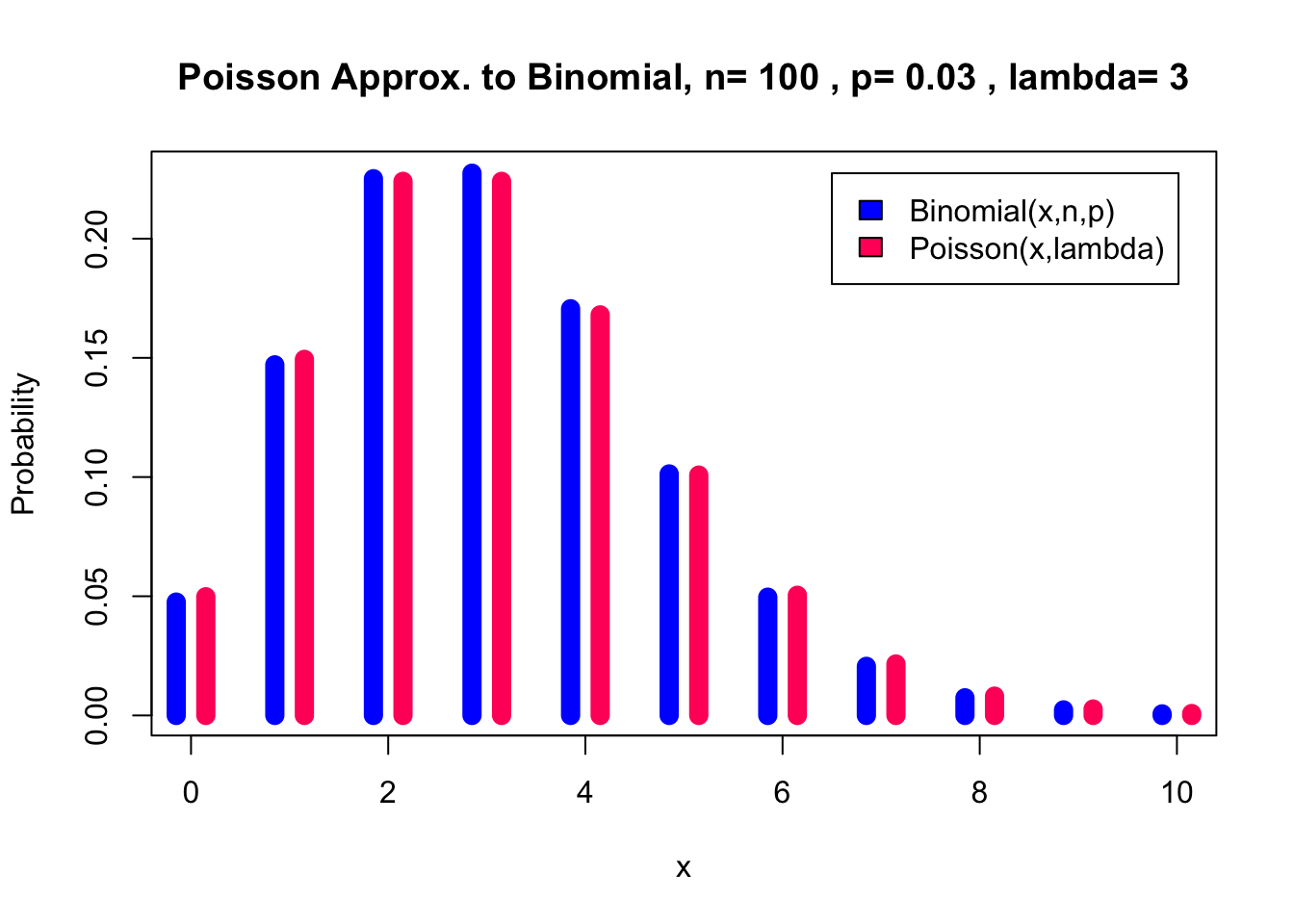
The Poisson distribution is actually a limiting case of a Binomial distribution when the number of trials, n, gets very large and p, the probability of success, is small. As a rule of thumb, if n ≥ 100 n ≥ 100 and np ≤ 10 n p ≤ 10, the Poisson distribution (taking λ = np λ = n p) can provide a very good approximation to the binomial.
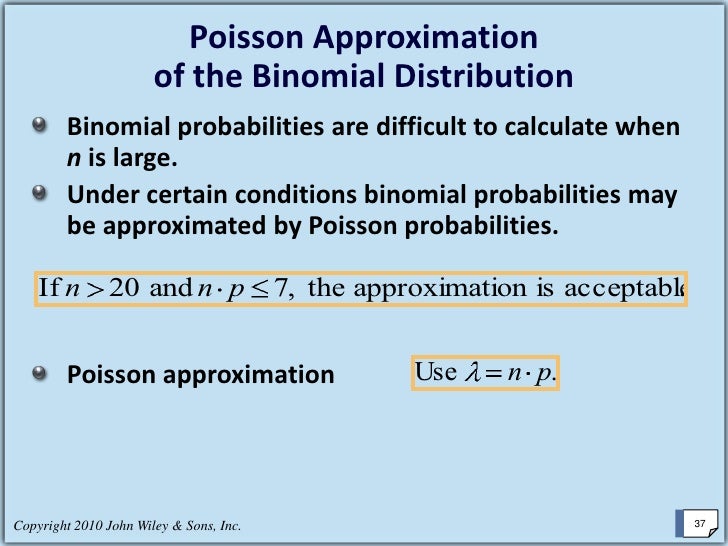
PPT Poisson approximation to a Binomial distribution PowerPoint Presentation ID517060

MIT RES.6-012 Introduction to Probability, Spring 2018View the complete course: https://ocw.mit.edu/RES-6-012S18Instructor: John TsitsiklisLicense: Creative.
Poisson binomial distribution MATLAB Mathematics Stack Exchange

More importantly, since we have been talking here about using the Poisson distribution to approximate the binomial distribution, we should probably compare our results. When we used the binomial distribution, we deemed \ (P (X\le 3)=0.258\), and when we used the Poisson distribution, we deemed \ (P (X\le 3)=0.265\).
The Relationship Between the Binomial and Poisson Distributions YouTube

So, it seems reasonable then that the Poisson p.m.f. would serve as a reasonable approximation to the binomial p.m.f. when your n is large (and therefore, p is small). Let's calculate P ( X ≤ 3) using the Poisson distribution and see how close we get. Well, the probability of success was defined to be: p = λ n. Therefore, the mean λ is: λ.
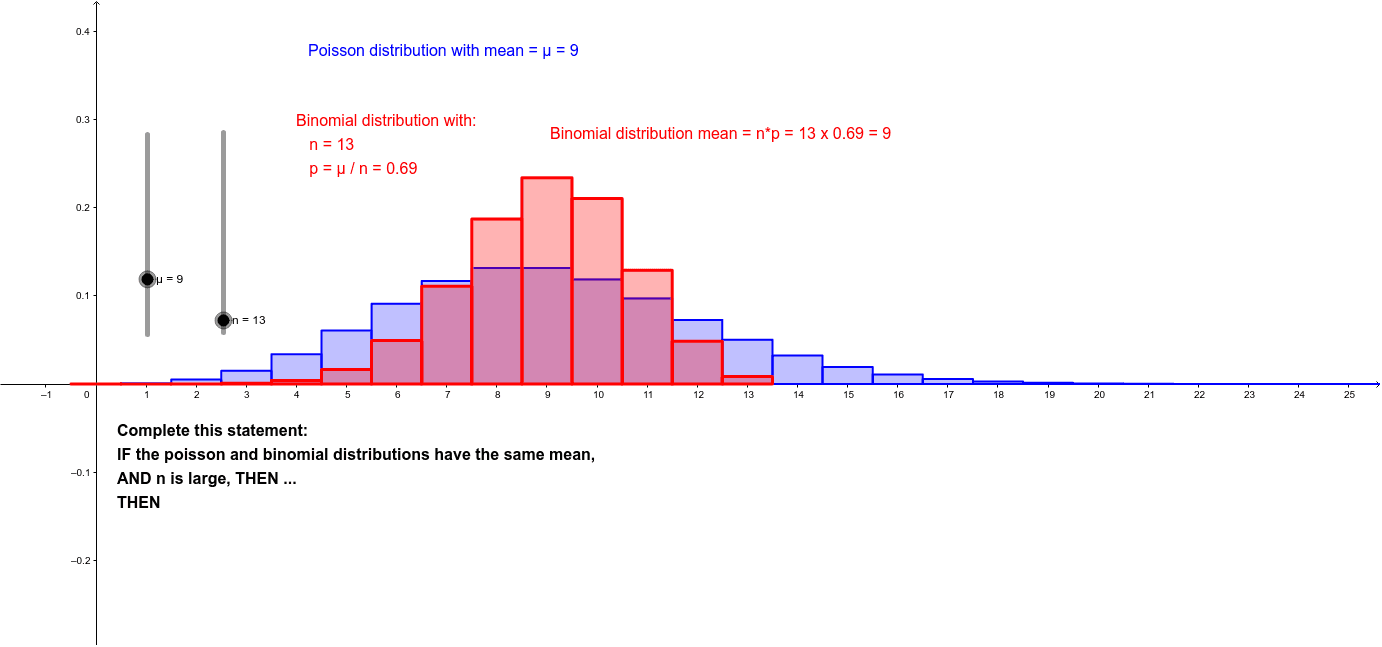
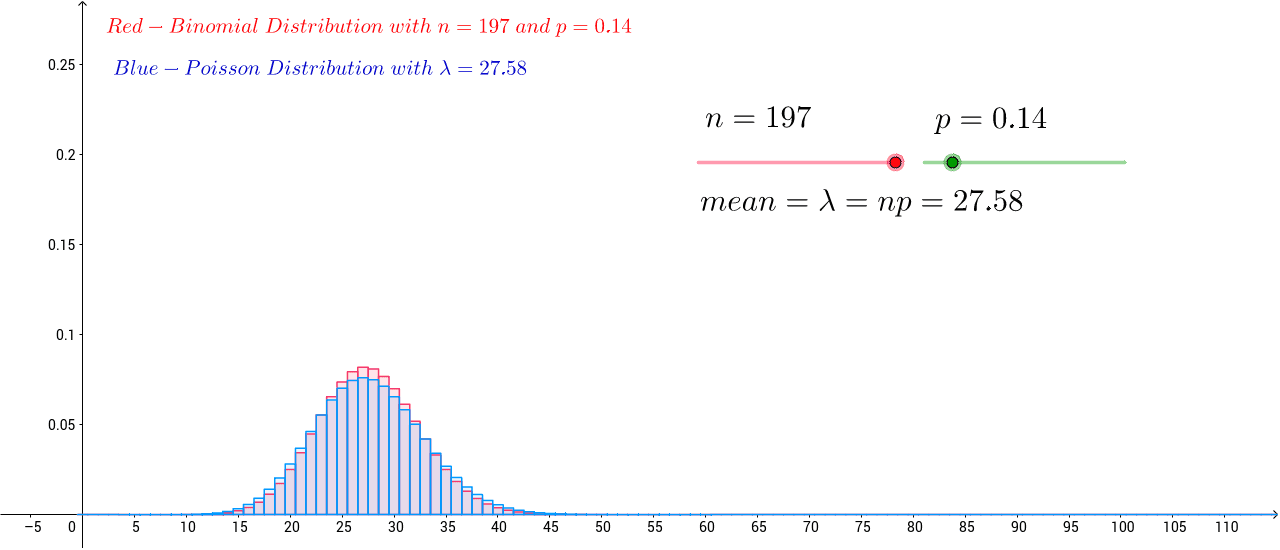
Poisson and Binomial Distributions Compare GeoGebra
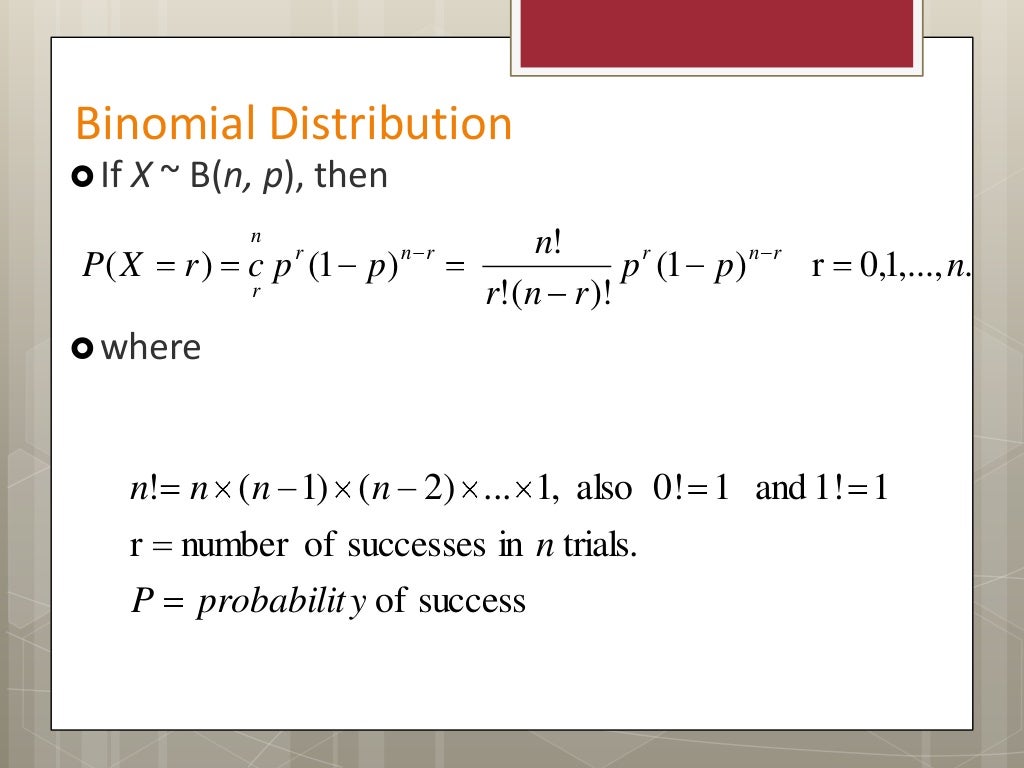
The Binomial Distribution. The Binomial distribution describes the probability of obtaining k successes in n binomial experiments. If a random variable X follows a binomial distribution, then the probability that X = k successes can be found by the following formula: P(X=k) = n C k * p k * (1-p) n-k. where: n: number of trials; k: number of.
Lecture 4 Poisson Approximation to Binomial Distribution
Poisson approximations 9.1Overview The Bin(n;p) can be thought of as the distribution of a sum of independent indicator random variables X 1 + + X n, with fX i= 1gdenoting a head on the ith toss of a coin that lands heads with probability p. Each X i has a Ber(p) distribution. The normal approximation to the Binomial works
[Math] Conditions for Normal Approximation to Binomial Math Solves Everything

I was reading Introduction to Probability Models 11th Edition and saw this proof of why Poisson Distribution is the approximation of Binomial Distribution when n is large and p is small: An import.
Normal Distribution, Binomial Distribution, Poisson Distribution
The Poisson Approximation. The Poisson process on \( [0, \infty) \), named for Simeon Poisson, is a model for random points in continuous time.. From a practical point of view, the convergence of the binomial distribution to the Poisson means that if the number of trials \(n\).
Poisson Approximation to the Binomial Distribution (Example) ExamSolutions Maths Revision

The Poisson binomial distribution has a variety of applications such as reliability analysis [16, 57], survey sampling [29, 104], nance [40, 92], and engineering [44, 100]. Though this. In this section, we discuss various approximations of the Poisson binomial distribution. Pitman [78, Section 2] gave an excellent survey on this topic in the.
probability How to prove Poisson Distribution is the approximation of Binomial Distribution

The idea behind Poisson approximation to the binomial distribution was used in de la Cal and Luquin (J Approx Theory 68(3):322-329, 1992) and subsequent papers in order to establish the convergence of suitable sequences of positive linear operators. The proofs in these papers are given using probabilistic methods. We use similar methods, but in analytic terms. In this way we recover some.
Approximating Binomial with Poisson
The most important sections in this chapter overall are Sections 2, 5, and 6. This section, together with 6, is about 50% of the most important material of the chapter. Before we start reading, let me give you an introduction. The subject of this section (the Poisson approximation) refers to a situation like Puzzle 1 in the introductory lecture.
Poisson Approximation to Binomial Distribution GeoGebra
The mean of X is μ = E(X) = np and variance of X is σ2 = V(X) = np(1 − p). The general rule of thumb to use Poisson approximation to binomial distribution is that the sample size n is sufficiently large and p is sufficiently small such that λ = np (finite). For sufficiently large n and small p, X ∼ P(λ). The probability mass function of.
PPT Probability and Probability Distributions PowerPoint Presentation ID5681061

Poisson limit theorem. In probability theory, the law of rare events or Poisson limit theorem states that the Poisson distribution may be used as an approximation to the binomial distribution, under certain conditions. [1] The theorem was named after Siméon Denis Poisson (1781-1840). A generalization of this theorem is Le Cam's theorem .
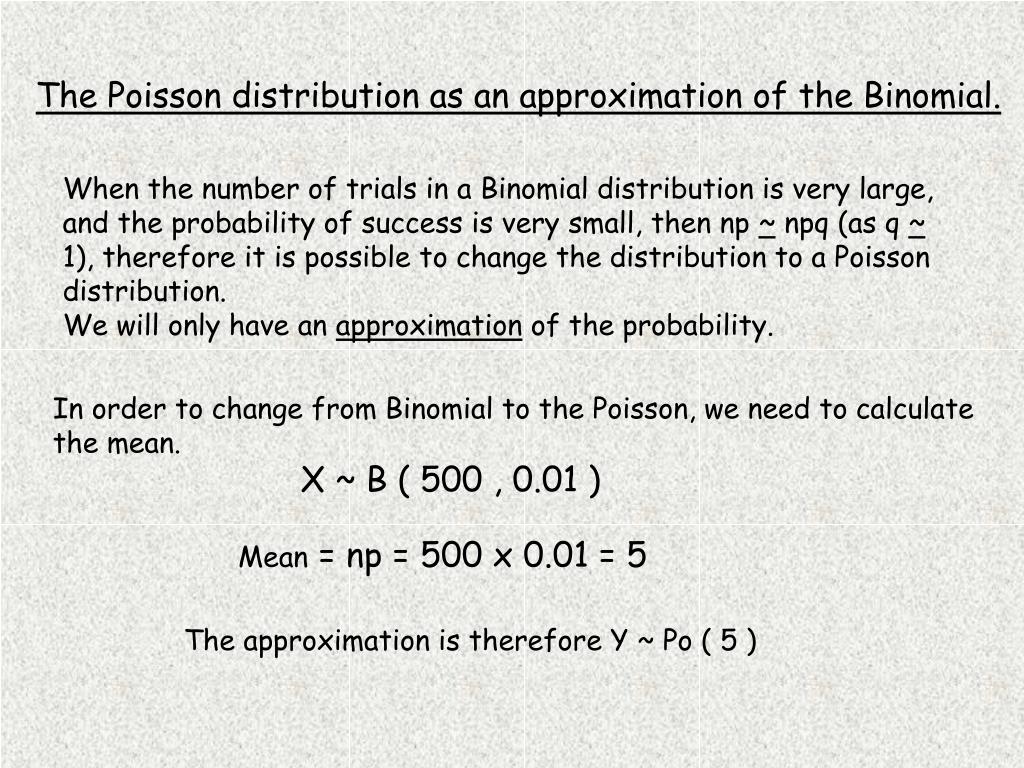
PPT The Poisson distribution as an approximation of the Binomial. PowerPoint Presentation ID
We use this approximation to the Binomial when p is very small and n is very large since = np tends to be reasonable. Statistics 104 (Colin Rundel) Lecture 7 February 6, 2012 8 / 26 Chapter 2.4-2.5 Poisson Poisson Distribution - Mode We can use the same approach that we used with the Binomial distribution 1 P(X = k + 1) P(X = k) k k! e (k+1) (k.
Probability Distributions Uniform, Binomial, Poisson, Normal YouTube

The defining characteristic of a Poisson distribution is that its mean and variance are identical. In a binomial sampling distribution, this condition is approximated as p becomes very small, providing that n is relatively large. The mean and variance of a binomial sampling distribution are equal to np and npq, respectively (with q=1—p). As p.
Discrete Probability Distributions
The Poisson distribution is a good approximation of the binomial distribution if n is at least 20 and p is smaller than or equal to 0.05, and an excellent approximation if n ≥ 100 and n p ≤ 10. [31] Letting and be the respective cumulative density functions of the binomial and Poisson distributions, one has:
.